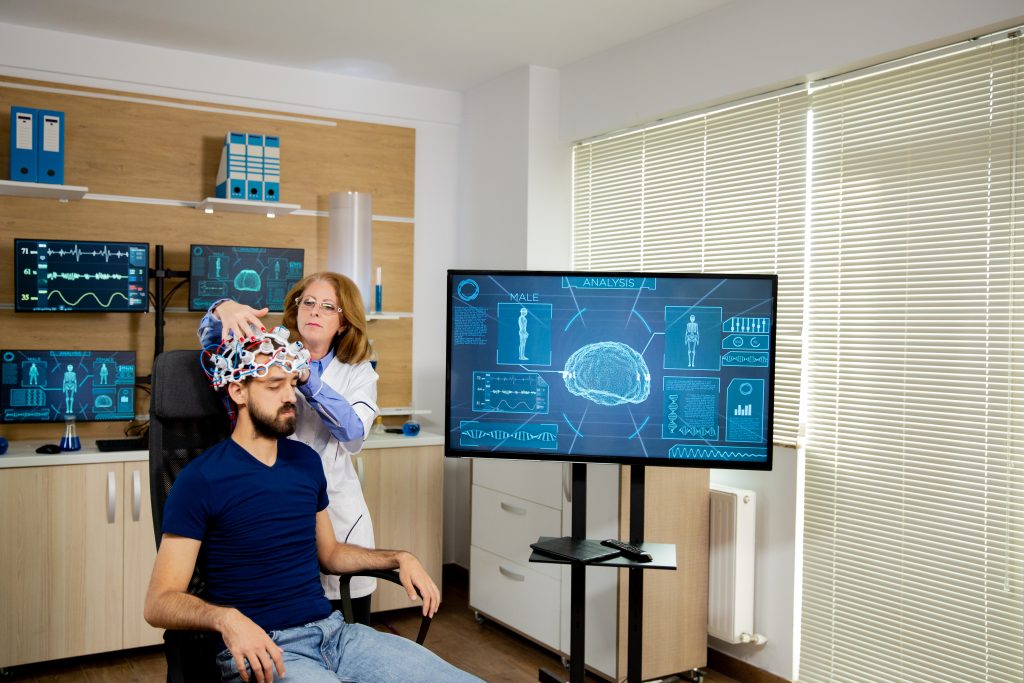
Neuralink Unveils Ambitious BCI Roadmap, Expands UK Clinical Trials
Elon Musk’s Neuralink has announced a groundbreaking 2025–2028 development plan, aiming to decode silent speech by Q4 2025 through cortical implants, followed by visual restoration for the blind in 2026 using its Blindsight system. The company’s N1 chip, already implanted in seven U.S. patients with spinal cord injuries or ALS, enables mind-controlled cursor navigation and gaming with 97% accuracy. In a parallel move, Neuralink launched its first UK trial, GB-PRIME, at University College London Hospitals, enrolling patients with paralysis to test wireless brain implants capable of controlling smartphones and computers via neural signals.
Notably, Neuralink’s long-term vision includes 25,000+ electrode channels by 2028 for treating psychiatric disorders and integrating with AI, potentially enabling direct human control of Tesla’s Optimus robots. While critics highlight the need for peer-reviewed data, the company’s progress underscores BCI’s transformative potential in neurological rehabilitation.

Graphene-Based BCI Achieves Milestone in Brain Tumor Surgery
Spanish firm INBRAIN Neuroelectronics revealed mid-term results from its global first-in-human trial of graphene-based brain-computer interfaces. The device, tested in four patients undergoing brain tumor resection, demonstrated sub-millisecond signal resolution and compatibility with clinical neurophysiology systems. Ultra-thin graphene electrodes captured high-gamma neural activity linked to speech phonemes with unprecedented precision, offering surgeons real-time guidance to preserve critical brain functions during tumor removal.
“This technology could redefine neurosurgical precision,” stated David Coope, lead neurosurgeon at Manchester University. Graphene’s biocompatibility and flexibility also hold promise for chronic neurological conditions like Parkinson’s.
AI Revolutionizes Drug Discovery and Diagnostic Accuracy
Google’s MedGemma, an open-source AI model launched at I/O 2025, combines 4B-parameter multimodal analysis for medical imaging with a 27B-parameter clinical text interpreter, achieving 99.1% accuracy in brain tumor diagnosis from cerebrospinal fluid samples. Meanwhile, Isomorphic Labs—spun off from DeepMind—advanced its AlphaFold 3-driven drug candidate into human trials, targeting fibrosis with an 18-month development cycle, a fraction of traditional timelines.
In clinical diagnostics, Germany’s CrossNN model reduced biopsy reliance by 30% through epigenetic analysis, while the U.S.-developed Chest CT AI Agent detected 73 thoracic conditions with industry-leading accuracy, deployed in 400+ hospitals.
Japan Pioneers Memory-Implanting BCI for Alzheimer‘s
Japanese researchers at RIKEN and the University of Tokyo unveiled a flexible neural synapse chip capable of encoding and storing memory fragments in the hippocampus. In preclinical trials, the device restored 40% of episodic memory in Alzheimer’s-affected macaques by mimicking neuronal firing patterns. The technology, now entering human trials, uses 128 nanoelectrodes to record and replay memory-related neural signals, marking a leap toward functional memory restoration.
Australian Innovations in Biohybrid Computing and Diabetes Care
Australian startup Cortical Labs launched CL1, the world’s first commercial biohybrid computer, integrating human neurons with silicon chips for energy-efficient, adaptive computing. The device’s self-organizing neural networks show potential for personalized brain training and drug discovery. Concurrently, ReShape Lifesciences secured an Australian patent for its vBloc™ neurostimulation system, which dynamically regulates pancreatic activity via vagus nerve stimulation, achieving 92% glycemic control in preclinical models of type 2 diabetes.
Ethical Frameworks and Global Policy Shifts
The EU’s Neuro Rights Charter took effect in 2025, banning commercial entities from accessing raw brain data without explicit consent and mandating ethical reviews for BCI trials. In the U.S., the FDA approved Neuralink’s expanded trials under strict safety protocols, while the UK’s MHRA emphasized patient autonomy in BCI research.
Upcoming Conferences: Catalysts for Innovation
The AI in Healthcare Congress (Lisbon, August 2025) and AIMI Symposium (Stanford, June 2025) will showcase cutting-edge applications, including AI-driven pediatric diagnostics and neuroethical frameworks. These events highlight the growing convergence of AI, BCI, and regulatory science.
From Neuralink’s speech-decoding ambitions to INBRAIN’s graphene breakthroughs, 2025 is witnessing unprecedented advancements in AI and BCI. These technologies not only address unmet medical needs but also challenge societal norms, urging stakeholders to balance innovation with ethical safeguards. As clinical trials expand and policies evolve, the global healthcare landscape stands on the cusp of a transformative era.




